Step1 : Create sample database
create database wes_db;
use wes_db;
create table wes_engineer(WES_ID integer, WES_NAME varchar(30));
insert into wes_engineer values(1, 'Amy');
insert into wes_engineer values(2, 'Alfred');
Step2 : Create carbon data-source
To be able to refer Carbon data-source within a web-app, first you need to register your Carbon data-source with a JNDI naming service. When you creating a carbon data-source there is option to select data-source repository type. From there select JNDI as repository and provide the jndi_context_class and the provider_url. You can use "com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory" JNDI service provider inside Carbon server.
Image 01: Adding Carbon data-source
Step3 : Create a simple web-app
This simple web app will access the above data-source and print all data available in wes_engineer table.
Once you registered your carbon data-source with a JNDI service, you can access that data-source directly within your web application by doing a JNDI lookup. Following code segment will illustrate you how to call carbon data-source within web-app.
Hashtable env = new Hashtable();
env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory"); //same context factory class provided when creating carbon data-source.
env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "rmi://localhost:2195"); //same provider url provided when creating carbon data-source.
InitialContext ctx = new InitialContext(env);
DataSource ds = (DataSource) ctx.lookup("jndiDS"); //"jndiDS" is the carbon data-source name that i have created. Please note that you may need to add commons-dbcp.jar and commons-pool.jar to web-app class path to do this cast.
conn = ds.getConnection();The full TestCarbonDataSource.java servlet class and project web.xml files are provided below.
TestCarbonDataSource.java
package org.wso2;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.*;
public class TestCarbonDataSource extends HttpServlet {
public TestCarbonDataSource() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
performTask(request, response);
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
performTask(request, response);
}
private void performTask(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<br/>");
out.println(testJndiDataSource());
}
public String testJndiDataSource() {
Connection conn = null;
Statement st = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
try {
Hashtable env = new Hashtable();
env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory");
env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "rmi://localhost:2195");
InitialContext ctx = new InitialContext(env);
DataSource ds = (DataSource) ctx.lookup("jndiDS");
conn = ds.getConnection();
st = conn.createStatement();
rs = st.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM wes_engineer");
while (rs.next()) {
String id = rs.getString("WES_ID");
String firstName = rs.getString("WES_NAME");
sb.append("ID: " + id + ", First Name: " + firstName + "
");
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try { if (rs != null) rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
try { if (st != null) st.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
try { if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
web.xmlOnce you create web-app, you can host it in WSO2 Application Server or any other application servers.<web-app> <servlet> <servlet-name>TestCarbonDataSource</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.wso2.TestCarbonDataSource</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>TestCarbonDataSource</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
Image 02: Deploy web-app in Application server.
Once web-app is deployed in Application server click on "Go To URL" link or directly go to the link using browser "http://localhost:9763/carbonDSwebApp/"
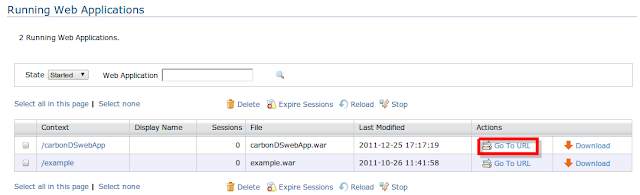
Image 03: Accessing web-app
You can see the output as bellow.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.