WSO2 Cipher Tool can be used to encrypt the plain text values provided in product configuration files or any other plain text value using product's keystore.
Sometimes, for troubleshooting purposes we need to decrypt this encrypted text and see whether it contains the correct plain text. There is no default client comes with WSO2 products to do this.
This post provides a client that can be used to decrypt and get the plain text value from encrypted text.
1. Download the pre-built client jar from here or you can checkout the source from here and build the project from source.
If you are building from source, clone the repo locally and execute "mvn clean install" to build it. This will create a executable jar called 'org.wso2.samples.decrypt-1.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar' in the target directory.
2. You can execute downloaded org.wso2.samples.decrypt-1.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar in two ways.
(i) Provide inputs as command arguments.
Command for this is;
java -jar org.wso2.samples.decrypt-1.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar $CipherText $KeystorePath $KeystoreAlias $KeystorePassword
eg: java -jar org.wso2.samples.decrypt-1.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar bBa173t6ThRLQOt6Z5BztDC56MXLAwb9cr6gHRJhWSbAGbIG7KaFxNjAuh9pVt/74tY06yKEt /SIgL42QDMQMmMjMgmd9KP9VMtVTMw2EMdW55VETgwHmPzfAiL242M77bpZW/Y9/YTanPQk8KStOxIUI4iAM42lm2z3imbHVh0= /home/dinusha/wso2is-5.3.0/repository/resources/security/wso2carbon.jks wso2carbon wso2carbon
If it executed successfully, decrypted value will be printed something similar to follows.
*** Plain Text ***
dinusha
******************
(ii) Execute as interactive command line inputs
Command for this is (Inputs will be asked one by one);
java -jar org.wso2.samples.decrypt-1.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar
Encrypted Text : bBa173t6ThRLQOt6Z5BztDC56MXLAwb9cr6gHRJhWSbAGbIG7KaFxNjAuh9pVt/74tY06yKEt/SIgL42QDMQMmMjMgmd9KP9VMtVTMw2EMdW55VETgwHmPzfAiL242M77bpZW/Y9/YTanPQk8KStOxIUI4iAM42lm2z3imbHVh0=
KeyStore file path : /home/dinusha/wso2is-5.3.0/repository/resources/security/wso2carbon.jks
KeyStore alias : wso2carbon
KeyStore password : wso2carbon
If it executed successfully, decripted value will be printed something similar to follows.
*** Plain Text ***
dinusha
******************
Hope this client will help you for troubleshooting!
Dinusha's Blog
Monday, April 2, 2018
WSO2 API Manager Gateway Extension points
WSO2 API Manager Gateway provides a synapse based runtime, which is similar to the WSO2 ESB runtime. Default mediation flow of the gateway can be extended with different extensions. Three main extensions are listed bellow.
[1] Custom Sequences - https://docs.wso2.com/display/AM210/Adding+Mediation+Extensions
[2] Custom API Handlers - https://docs.wso2.com/display/AM210/Writing+Custom+Handlers
[3] Custom Synapse Handlers - http://prabu-lk.blogspot.co.uk/2015/10/how-to-write-synapse-handler.html
Provided links contain details on how to implement each of above extensions. In this post we will discuss mainly the execution order of these extensions if someone has placed all of them. Hope that will help someone to understand which extension should be used for their use case and where to troubleshoot if you have any issues in the mediation flow.
You can implement concrete handler by implementing org.apache.synapse.SynapseHandler interface or can extends org.apache.synapse.AbstractSynapseHandler class.
There are four methods that you need to implement.
+handleRequestInFlow(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute just after request hitting to the synapse engine (API GW)
+handleRequestOutFlow(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute just before request dispatch to endpoint
+handleResponseInFlow(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute just after response received to API GW
+handleResponseOutFlow(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute just before response dispatch to client
Concrete implementation should be done by extending org.apache.synapse.rest.AbstractHandler class.
There are two method that you need to implement.
+handleRequest(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute in the request flow, before dispatching request to endpoint
+handleResponse(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute in the response flow, before dispatching response to client
[1] Custom Sequences - https://docs.wso2.com/display/AM210/Adding+Mediation+Extensions
[2] Custom API Handlers - https://docs.wso2.com/display/AM210/Writing+Custom+Handlers
[3] Custom Synapse Handlers - http://prabu-lk.blogspot.co.uk/2015/10/how-to-write-synapse-handler.html
Provided links contain details on how to implement each of above extensions. In this post we will discuss mainly the execution order of these extensions if someone has placed all of them. Hope that will help someone to understand which extension should be used for their use case and where to troubleshoot if you have any issues in the mediation flow.
Custom Synapse Handler
Global extension handler, which will execute for each API invocation. If someone needs to perform some actions for each and every API, then we could write a global synapse handler.You can implement concrete handler by implementing org.apache.synapse.SynapseHandler interface or can extends org.apache.synapse.AbstractSynapseHandler class.
There are four methods that you need to implement.
+handleRequestInFlow(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute just after request hitting to the synapse engine (API GW)
+handleRequestOutFlow(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute just before request dispatch to endpoint
+handleResponseInFlow(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute just after response received to API GW
+handleResponseOutFlow(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute just before response dispatch to client
Custom API Handler
Need to engage per API. If you need to engage handler of all the APIs, that can be done by editing velocity_template.xml provided in API Manager. Refer doc [2] provided above fore details.Concrete implementation should be done by extending org.apache.synapse.rest.AbstractHandler class.
There are two method that you need to implement.
+handleRequest(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute in the request flow, before dispatching request to endpoint
+handleResponse(MessageContext messageContext) - Execute in the response flow, before dispatching response to client
Custom Sequence
Synapse sequences . Can be engage in the request in flow or the response out flow. Sequence should be named in a convention. Refer doc [1] provided above.
Custom sequences are executed using a default handler (APIManagerExtensionHandler) provided in APIM. This handler has been places as the last handler in the API synapse definition. So that custom sequences are getting executed after executing all other handlers.
Execution Order
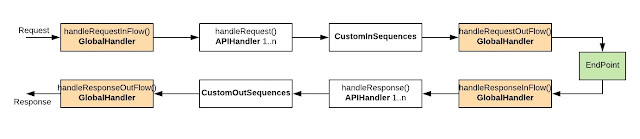
Following diagram explains the execution order if someone has Global synapse handler, Custom API handler, Custom IN/OUT sequences are deployed.
Request first hit the handleRequestInFlow() method of global synapse handler, then it goes through all the handleRequest() methods of all API handlers, then the custom IN sequences are getting executed, then it goes to handleRequestOutFlow() method of global synapse handler, and finally request getting dispatch to the endpoint.
Then the response sent by endpoint is getting first hit to the handlerResponseInFlow() method of global synapse handler, then it goes through all handleResponse() methods of all API handlers, then the custom OUT sequences are getting executed, then it goes to the handleResponseOutFlow() method of the global synapse handler, and finally response getting dispatch to the client.
Hope this post helps to understand the API Manager Gateway mediation extensions and execution order of them!
Friday, August 11, 2017
Amazon Web Services (AWS) integration with WSO2 Identity Server (WSO2 IS)
Overview
Amazon Web Services (AWS) supports federated authentication with SAML2 and OpenId Connect standards. This gives capability to login to AWS Management console or call the AWS APIs without having to create an IAM user in AWS for everyone in your organization.Benefits of using federated single sign on login for AWS access
- No need to create IAM users in AWS side
- If organization having existing user store, we can use it as the user base for AWS
- You can use single identity for user, all over the systems used by your organization
- This makes administrator life easier when user onboarding or offboarding to the organization
In this tutorial we are going to look at following integration scenarios;
- Connect WSO2 Identity Server (WSO2 IS) to single AWS account
- Connect WSO2 Identity Server to multiple AWS accounts
1. Connect WSO2 Identity Server to single AWS account
Business Use case : Your organization owns a AWS account and need to give different level of privilege access to AWS console to organization users.
How to configure WSO2 IS to support this: This tutorial explains the required steps for this including Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) https://medium.facilelogin.com/enable-fido-multi-factor-authentication-for-aws-management-console-with-wso2-identity-server-57f77e367f41
2. Connect WSO2 Identity Server to multiple AWS accounts
Business Use case : Your organization can owns multiple AWS accounts (eg: Development, Production), you need to assign different level of permissions in these accounts using the existing identity used for users in organization user store (ldap, jdbc etc).
How to configure WSO2 IS to support this:
Following tutorial explains required configurations for this.
Following tutorial explains required configurations for this.
We assume a user Alex in organization ldap, which need to give EC2 Admin permissions in development AWS account and need to have only EC2 read only access to the production AWS.
Business Requirements:
- Organization use WSO2 IS as the Identity Provider (IdP). Use same IdP to authenticate users to AWS Management console as well
- User Alex in organization should be able to log into development AWS account as an EC2 admin user
- Alex should be able to log into production AWS account using the same identity, but only with EC2 read only access
- Alex should be able to switch role from development account to production account
Configuration Guide
1. Configure AWS
1.1. Configure AWS Development Account
Step 1: Configure WSO2 IS as an Identity Provider in Development Account
a. Log into AWS console using development account, navigate to Services, then click on IAM
c. On the prompt window provide following info and click on "Create"
Provider Type : SAML
Provider Name: Any preferred name as identifier (eg:wso2is)
Metadata Document: Need to download WSO2 IS IdP metadata file and upload here. Following is the instructions to download IdP metadata file from WSO2 IS.
Login to WSO2 IS management console as admin user. Navigate to "Resident" under "Identity Providers" left menu. In the prompt window, expand the "Inbound Authentication Configuration", then expand the "SAML". There you can find the "Download SAML Metadata" option. Click on it, this will give option to save IdP medata in medata.xml file. Save it to local file system and upload it in AWS IdP configure UI as the Metadata Document.
AWS IdP configuring UI
d. Locate the Identity Provider that we created and make a copy of Provider ARN value. We need this value later in the configurations.
Step 2: Add AWS IAM roles and configure WSO2 IS Identity provider as trusted source in these roles
a. We need to create a AWS IAM role with EC2 Admin permissions since Alex should have EC2 Admin privileges in development AWS account.
Option 1 : If you have an existing role.
If you have an existing role with EC2Admin permissions, then we can edit the trust relationship of role by giving SSO access to WSO2 IS identity provider. If you do not have an exiting role, move to the option 2 which describes with adding a new role.
Click on the desired role -> Go to "Trust Relationships" tab and click on "Edit trust relationship"
If your current trust relationship policy is empty for this role, you can copy and replace following policy configuration there after replacing the <Provider ARN Value of IdP> value (i.e the Provider ARN value that you taken in step1)
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::<Provider ARN Value of IdP>:saml-provider/local-is"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithSAML",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"SAML:aud": "https://signin.aws.amazon.com/saml"
}
}
}
]
}
If you have a current policy in place, then you need to edit existing policy and include SSO access for WSO2 IS.
Option 2 : Create and assign permissions to a new role.
Option 2 : Create and assign permissions to a new role.
Go to "Roles" and Click on "Create new role". Select the role type as "Role for identity provider access" since we need to allow SSO access using WSO2 IS.
Select wso2is as the SAML provider and click Next.
On the next step just verify the trust policy and click on Next.
Select your preferred policy to be assigned to the role that you are creating. As per our sample scenario, we need to assign "AmazonEC2FullAccess" policy to give EC2 Admin permissions to this role.
Give a preferred role name and click on "Create". (eg: Dev_EC2_Admin)
b. Locate the Role ARN value in role summary page and make a copy of the value. We need this value later in the configurations.
Now we have configured WSO2 IS as a SAML Identity Provider for development AWS account and also created a role with EC2 full access permissions allowing sts:AssumeRoleWithSAML capability to WSO2IS saml-provider.
1.2. Configure AWS Production Account
Step 1 : We need to repeat the same step we did for development account previously with the step 1 and configure WSO2 IS as an Identity Provider for production account as well.Step 2 : Similar to we created Dev_EC2_Admin role in development account, we need to create EC2ReadOnly role in production AWS account. (As per our sample scenario, Alex should have EC2 read only access to the production AWS account). Only difference is you need to select the appropriate policy (AmazonEC2ReadOnlyAccess) for this role. Refer following which highlights only this step.
Once the role is created, make a copy of Role ARN value of this role as well. We need this value later in the configurations.
1.3. Configure account switch capability from AWS development account's Dev_EC2_Admin role to production account's Prod_EC2_ReadOnly role
a. Login to the AWS development account and configure an IAM policy that grants privilege to call sts:AssumeRole for the role that you want to assume (i.e we need to assume Prod_EC2_ReadOnly role in production account). To do this,1. Select "Policies" in the left menu and click on "Create Policy" option. Pick the "Create Your Own Policy" option there.
2. Give a relevant name for policy name and copy the following policy configuration after replacing <Prod_AWS_Account_Id> and <Prod_AWS_EC2_ReadOnly_Role> values as the content.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole",
"Resource": "arn:aws:iam::Prod_AWS_Account_Id:role/Prod_AWS_EC2_ReadOnly_Role"
}
]
}
3. Attach the policy that we created in previous step to Dev_EC2_Admin role in development account. For this, click on the role name and click on "Attach Policy" in resulting window.
Now we have given permissions to Dev_EC2_Admin role in development AWS account to to assume the role Prod_EC2_ReadOnly in production account.
b. Login to the production AWS account and edit the trust relationship of role Prod_EC2_ReadOnly, by adding development account as a trust entry. To do this,
1. Click on the role name "Prod_EC2_ReadOnly" and navigate to "Trust relationships" tab and click on "Edit trust relationship" option.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::222222222222:saml-provider/wso2is-local"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithSAML",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"SAML:aud": "https://signin.aws.amazon.com/saml"
}
}
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::<Dev_Account_Id>:root"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
We are done with the AWS configurations. We need to configure WSO2 IS to SSO with these two accounts now.
2. Configure AWS app in WSO2 IS
1. Login to the WSO2 IS Management console, then navigate to Main -> Service Providers -> Add from the left menu. Provide any proffered name to "Service provider name" (eg: AWS) and click on register.2. In the resulting window, expand the "Claim Configuration" section, then select the "Define Custom Claim Dialect" option and do following claim mapping.
https://aws.amazon.com/SAML/Attributes/Role -> http://wso2.org/claims/role https://aws.amazon.com/SAML/Attributes/RoleSessionName -> http://wso2.org/claims/emailaddress
3. Expand the "Role/Permission Configuration", then "Role Mapping" and add following role mappings.
What we do here is, map local roles in wso2is to AWS roles. We have two ldap roles called "dev_aws_ec2_admin" and "prod_aws_ec2_readonly" which assigned to organization users to give required access to AWS developer and production account.
When you do the mapping pick relevant role in your organization user store instead of dev_aws_ec2_admin and prod_aws_ec2_readonly. Also relevant Role ARN and Provider ARN values from each account.
dev_aws_ec2_admin -> Role_ARN_Of_Developemnt_Account,Provider_ARN_Of_Development_Account prod_aws_ec2_readonly -> Role_ARN_Of_Production_Account,Provider_ARN_Of_Production_Accounteg:
dev_aws_ec2_admin -> arn:aws:iam::222222222222:role/Dev_EC2_Admin,arn:aws:iam::222222222222:saml-provider/local-is
prod_aws_ec2_readonly -> arn:aws:iam::111111111111:role/Prod_EC2_ReadOnly,arn:aws:iam::111111111111:saml-provider/wso2is-local
4. Expand the "Inbound Authentication Configuration", under that "SAML2 Web SSO Configuration" and select "Configure".
In the configuration UI, provide following fields and click update.
Issuer : urn:amazon:webservices Default Assertion Consumer URL : https://signin.aws.amazon.com/saml Enable Attribute Profile: Checked Include Attributes in the Response Always: Checked Enable IdP Initiated SSO: Checked
5. Open the IS_HOME/repository/conf/user-mgt.xml and find the active user store configuration there. Change the MultiAttributeSeparator value to something different from comma (,) and restart the server.
Example:
<Property name="MultiAttributeSeparator">$$</Property>
Why we need to change this MultiAttributeSeparator value is, this property is used to separate the multiple attributes. By default this is set to a comma (,). But since we need to use AWS Role ARN, Provider ARN as a single value, we need to change it's value to something different from comma.
We are done with all configurations.
3. Testing
1. Before access AWS console, login to the WSO2 IS Management console and confirm whether user Alex is having required roles assigned. Also Alex's user profile has been updated with his email address which mapped as RoleSessionName claim in AWS.2. Access the AWS console using following url. (Replace the <WSO2IS-HOST>:<PORT> as relevant).
https://<WSO2IS-HOST>:<PORT>/samlsso?spEntityID=urn:amazon:webservices
3. Previous step will redirect you to WSO2 IS login page and once user Alex provided credentials and authenticated, AWS will provide it's role selection page where user can pick the role for current session and continue.
4. Alex can switch role from development account to production role using either switch role option provided in AWS console or the Switch Role URL associated to AWS role.
AWS switch role url can be found in the role detail. Usually this is in the format of;
https://signin.aws.amazon.com/switchrole?account=<AWS_ACCOUNT_ID>&roleName=<AWS_ROLE_NAME>
If you provide production account id and role as "Prod_EC2_ReadOnly" in the above URL, you can see that Alex can switch to production account's Prod_EC2_ReadOnly role from development account where he was logged in.
Monday, May 29, 2017
Configure Single Sign On (SSO) for a Web App Using WSO2 Identity Cloud and Consume APIs Published in WSO2 API Cloud Using JWT Bearer Grant Type
WSO2 Cloud provides comprehensive set of cloud solutions, This includes; Identity Cloud, API Cloud, Integration Cloud and Device Cloud. Identity Cloud provides security while API Cloud provides API Management solution (In near future identity Cloud is going to provide full set of IAM solutions, where at the moment (May 2017) it has only supports Single Sign On). In real world scenarios, application security and API security goes hand in hand where most of the time these web apps need to consume secured APIs.
In this post, we are going to look at how we can configure security for a web app with WSO2 Identity Cloud and that application needs to consume some OAuth protected APIs published in WSO2 API Cloud.
If you need to configure SSO for a application with WSO2 identity Cloud, you need to configure a service provider in Identity Cloud representing your application. Document https://docs.wso2.com/display/IdentityCloud/Tutorials explains the services provider configuration options in detail. If you are configuring SSO for a your own application (not a pre-defined app like Salesfoce, AWS etc), there are two main options provided, that you can select. Those are "Agent based SSO" and "Proxy based SSO". Post http://dinushasblog.blogspot.com/2017/05/what-is-agent-and-proxy-based-sso-in.html explains what these two options are and when to choose which option, in detail.
Here, we are going to use Proxy based SSO option and configure SSO for a java web application. Once user is authenticated to access the application, Identity Cloud sends a signed JSON Web Token (JWT token) to the backend application. This JWT token can be used with JWT bearer grant type to get an access token from API Cloud to consume APIs publish there.
Before that, what is JWT bearer grant type;
JWT bearer grant type provides a way for client application to request an access token from OAuth server, using an existing proof of authentication in the form of a signed claims which was done by different Identity Provider. In our case, Identity Cloud is the JWT token provider while API Cloud is the one provide OAuth acess tokens.
i. Login to Identity Cloud admin portal : https://identity.cloud.wso2.com/admin
ii. Add New Application (Note: Select the "Proxy" as app type)
In this post, we are going to look at how we can configure security for a web app with WSO2 Identity Cloud and that application needs to consume some OAuth protected APIs published in WSO2 API Cloud.
If you need to configure SSO for a application with WSO2 identity Cloud, you need to configure a service provider in Identity Cloud representing your application. Document https://docs.wso2.com/display/IdentityCloud/Tutorials explains the services provider configuration options in detail. If you are configuring SSO for a your own application (not a pre-defined app like Salesfoce, AWS etc), there are two main options provided, that you can select. Those are "Agent based SSO" and "Proxy based SSO". Post http://dinushasblog.blogspot.com/2017/05/what-is-agent-and-proxy-based-sso-in.html explains what these two options are and when to choose which option, in detail.
Here, we are going to use Proxy based SSO option and configure SSO for a java web application. Once user is authenticated to access the application, Identity Cloud sends a signed JSON Web Token (JWT token) to the backend application. This JWT token can be used with JWT bearer grant type to get an access token from API Cloud to consume APIs publish there.
Before that, what is JWT bearer grant type;
JWT bearer grant type provides a way for client application to request an access token from OAuth server, using an existing proof of authentication in the form of a signed claims which was done by different Identity Provider. In our case, Identity Cloud is the JWT token provider while API Cloud is the one provide OAuth acess tokens.
Step 1: Configure Service Provider in Identity Cloud
i. Login to Identity Cloud admin portal : https://identity.cloud.wso2.com/admin
ii. Add New Application (Note: Select the "Proxy" as app type)
iii. Go to user-portal of tenant. (I'm using wso2org as the tenant, hence my user-portal is https://identity.cloud.wso2.com/user-portal/t/wso2org). This will list the application there and if you click on it, you can invoke it. Note that application URL is not the real endpoint URL of application that used to invoke it. This is because, since we used "Proxy" option, Identity Cloud acts as a proxy for this app and gives a proxy URL (also called as gateway URL).
You need to block the direct app invocations using firewall rule or nginx rule to make sure, all users can access application only through Identity Gateway with the provided proxy URL. Following diagram explains what really happens there.
That's all we have to do to get SSO configured for your web application with Identity Cloud using proxy option. In summary, you login to Identity Cloud admin portal, register a new application (service provider) there by providing your web app endpoint url and provide a new url context to get gateway url constructed. Gateway do the SAML authentication part on behalf of application.
Step 2 : Use JWT Token sends by Identity Cloud to backend and get a access token from API Cloud to invoke APIs
Backend web app needs to consume some APIs published in API Cloud. But the user authentication for web app happened from Identity Cloud, how can it get a access token from API Cloud ? We can use JWT Bearer Grant type for that, since Identity Cloud gives a JWT token after user authentication.
This JWT token should contains API Cloud as an audience, if it need to be consumed by API Cloud.
i. Edit the service provider (application) which was registered in Identity Cloud and add API Cloud's key manager endpoint as an audience.
Service provider configuring UI provided in Identity Cloud admin portal does not have option to add audiences for proxy type apps (which should be fixed in UI). Until that we need to login to the carbon management console of Identity Cloud and configure it.
NOTE : Carbon mgt UIs of WSO2 Cloud are not exposed to everyone. You need to contact wso2 cloud support by filling form https://cloudmgt.cloud.wso2.com/cloudmgt/site/pages/contact-us.jag to get carbon mgt UI access.
In the Carbon UI, navigate to Main -> Service Providers -> List -> Click Edit of Service provider that you created. Inbound Authentication configuration -> SAML -> Audience URLs -> Add "https://keymanager.api.cloudstaging.wso2.com/oauth2/token" as audience and update the SP. Refer following image.
ii. Configure Identity Cloud as a trusted IdP in API Cloud.
API Cloud should trust Identity Cloud as a trusted IdP, if it needs to issue an access token using JWT token issued by Identity Cloud. We need to login to Carbon UI of API Cloud's Key Manager and configure Identity Cloud as a trusted IdP.
NOTE : You need to contact wso2 cloud support by filling form https://cloudmgt.cloud.wso2.com/cloudmgt/site/pages/contact-us.jag to get carbon mgt UI access of API Cloud's Key Manager.
Navigate to Main -> Identity Providers -> Add -> Give the IdP details and Save
Identity Provider Name : wso2.org/products/appm
Identity Provider Public Certificate : Need to upload your tenant's public certificate here. You can get this by login to the admin portal of Identity Cloud and Click on "Download IdP Metadata" option provided in application listing page. This metadata file contains public certificate as a one metadata. You can copy and save certificate into a separate file and upload here.
Refer following image for add IdP.
Following images shows how you can download tenant's public certificate from Identity Cloud to upload above.
Downloaded metadata file will looks something similar following. Copy the certificate into a separate file and upload.
We are done with all configurations.
Step 3 : How to read the value of JWT Token and use it to request access token from API Cloud ?
JWT Token is sent to the backend in the header of "X-JWT-Assertion". Backend application can read the value of this header to get the JWT token.
Following image shows a sample JWT token printed by backend application by reading "X-JWT-Assertion" header.
Then backend application can use this JWT token and call to API Cloud token endpoint to get an access token using JWT bearer grant type. Before that you can copy this JWT token and use curl or some other REST client and test it.
curl -i -X POST -H "Authorization:Basic <YOUR_Base64Encoded(ConcumerKey:ClientSecreat)>" -k -d 'grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&assertion=<YOUR_JWT_TOKEN_HERE>' -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' https://gateway.api.cloud.wso2.com:443/token
This should provide you a oauth access token from API Cloud.
That's it !
Reference to sample web application code: https://github.com/dinusha-dilrukshi/wso2-integration-scenarios
This sample web app contains whole scenario described in this post. Try it too.
Sunday, May 28, 2017
What is Agent and Proxy Based SSO in WSO2 Identity Cloud ?
WSO2 Identity Cloud provides different options to easily configure Single Sign On (SSO) for your in-house enterprise applications and popular SaaS applications.
In the Service Provider configuration UI provided in Identity Cloud admin portal (https://identity.cloud.wso2.com/admin), you can see two options called "Agent" and "Proxy" that you need to select as App Type. Refer following image.
In this post we are going to look at a comparison of two options. So that it will help you to decide which option is suitable for your app.
In the Service Provider configuration UI provided in Identity Cloud admin portal (https://identity.cloud.wso2.com/admin), you can see two options called "Agent" and "Proxy" that you need to select as App Type. Refer following image.
In this post we are going to look at a comparison of two options. So that it will help you to decide which option is suitable for your app.
Agent based SSO (Agent Type)
- Authentication SSO request/response should be handled by application itself. We called this type as "Agent based" because, you can write a common separate module (agent) that can be used by all your applications to handle authentication.
eg: If you need to configure SSO for your application with SAML 2.0, then you should implement logic in your app to initiate SAML authentication request to Identity Cloud and Identity Cloud will send the authenticated SAML Response to application. Application should process this SAML response and identity the user and extract required user claims. (Note: With Service Provider Initiated SSO (SP init SSO), there is a way Identity Cloud to initialize the authentication request and application to handle only response sent by Identity Cloud )
- Supports SAML 2.0, WS-Federation, OpenID connect standard protocols.
- If the application already written to support these protocols, agent based option is the best fit. eg: Saleforce, AWS, Concur, GotoMeeting like SaaS application provides configuration options to configure federated authentication from IdPs using these standard protocols.
- Following diagram illustrate how Agent Type app authentication works.
Proxy based SSO (Proxy Type)
- Authentication SSO request/response are handled by the Identity Gateway. Application do not have to worry about it. Once user authenticated through Identity Gateway, it sends a signed JSON Web Token (JWT Token) containing authenticated user info to the backend app.
- Application is given a proxy URL instead of real endpoint URL of app. Users should use this proxy URL instead of direct app endpoint to access it.
- If application does not have internal logic based on authenticated user, you can simply publish the app as a Proxy app in Identity Cloud and done with it. This will ensures users cannot access this app, without authenticating from Identity Cloud.
eg: wso2.com (http://wso2.com) site does not need user authentication to see the content of it. If we need to give access only to authenticated users, we can publish (define) this as a proxy app in Identity Cloud. This will give a new proxy URL and that need authentication to access the site.
- Most of the time applications need user information for application side session handling and execute some business logic. In this case application should process the JWT token sent by identity Gateway and extract the user information.
- If you are trying to configure SSO for a well known SaaS app like Salesforce, AWS etc, then proxy type is not the option for it. Because, these apps expect authenticated user info and they do not have a way to process JWT token to get that info. Therefore mostly, Proxy Type can be used if you have control over modifying application source code.
- Following diagram illustrate how proxy app type based app works.
- Identity Gateway (Proxy based apps) capable in providing authorization as well to the application, not only authentication.
eg: It has capability to define rules like this,
- Application can be accessed only if authenticated user is having a particular role.
- Some of the resources in application should be allowed for selected roles, while other resources in app can be accessed by all authenticated users. (This can be done using role based or defining a XACML policy for that resource)
- Define throttling limits for resources based on number of access by user
NOTE: Identity Cloud admin portal does not provide UI for some of these gateway functionalities, even though identity Gateway has capability on handling them. UI will be improved to support them in future.
- Following diagram shows the handler sequence that get executed when accessing a app as a proxy type app.
Hope this post will help you to select which app type is suitable for you from Agent and Proxy types.
Saturday, February 25, 2017
WSO2 Identity Cloud in nutshell
WSO2 Identity Cloud is the latest addition to WSO2 public Cloud services. Identity Cloud is hosted using WSO2 Identity Server which provides Identity and Access Management (IAM) solution. Initial launching of Identity Cloud has been focused on providing Single Sign On (SSO) solutions for organizations.
All most all the organizations use different applications. This cloud be in-house developed and hosted applications or Salesforce, Councur, AWS like SaaS applications. Having centralized authentication system for all the applications will increase the efficiency of maintaining systems, centralize monitoring and company security from system administrative perspective while it makes application users life easy. WSO2 Identity Cloud provides solution to configure SSO for these applications.
What are the features offered by WSO2 Identity Cloud ?
- Single Sign On support with authentication standards - SAML-2.0, OpenID Connect, WS-Federation
Single Sign On configurations for applications can be done using SAML-2.0, OpenID Connect, WS-Federation protocols.
- Admin portal
Portal provided for organization administrators to login and configure security for applications. Simplified UI is provided with minimum configurations. Pre-defined templates of security configurations are available by default for most popular SaaS apps. This list includes Salesforce, Concur, Zuora, GotoMeeting, Netsuite, AWS. - On-premise-user-store agent
Organizations can connect local LDAP with Identity Cloud without sharing LDAP credentials with Identity Cloud and let users in organization LDAP to access applications with SSO. - Identity Gateway
Act as a simple application proxy that intercepts application requests and applies security checks. - User portal
User Portal provides a central location for the users of an organization to log in and discover applications in a central place, while applications can be accessed with single sign-on.
Why you should go for a Cloud solution ?
- Facilitating infrastructure - You don't have to spend money on additional infrastructure with the Cloud solution.
- System Maintenance difficulties - If you do a on-premise deployment, then there should be a dedicated team allocated to ensure the availability of system and troubleshoot issues etc. But with the Cloud solution WSO2 Cloud team will take care of system availability.
- Timelines - Identity Cloud is a already tested, up and running solution. This will cut off the deployment finalizing and testing times that you should spend on a on-premise deployment.
- Cost - No cost involve for infrastructure or maintenance with the Cloud solution.
We hope WSO2 Identity Cloud can help building a Identity Management solution for your organization. Register and tryout for free -http://wso2.com/cloud/ and give us your feedback on bizdev@wso2.com or dev@wso2.org.
Wednesday, June 29, 2016
How to configure WSO2 App Manager with MySQL ?
All WSO2 products comes with H2 internal database/s by default. Any of these product can be configured with different databases other than the H2 DB. App Manager product contains several databases unique only to App Manager that is not common with other WSO2 products. If you are familiar with changing default database of any of WSO2 product, concept is similar for App Manager as well. Anyway, here I'm explaining step by step, what each of these database in App Manager is doing and how we can configure them to use MySQL.
We have following five datasources defined in the {AppM_Home}/repository/conf/datasources/master-datasources.xml file.
[1] <name>jdbc/WSO2CarbonDB</name> - Use for registry data storage, user store, permission store
[2] <name>jdbc/WSO2AM_DB</name> - Use to store App details that created from App Manager
[3] <name>jdbc/WSO2AM_STATS_DB</name> - Stats storage. Needed only when Data Analytic Server is configured
[4] <name>jdbc/ES_Storage</name> - Use to store thumbnail/banner images of apps
[5] <name>jdbc/WSO2SocialDB</name> - Use to store comments and ratings added for apps by store users
This guide explains configuring App Manager standalone instance with MySQL DB. If it is a cluster deployment, there are some additional configurations required other than explains in this post.
Step 0: Login to the MySQL server and create 4 databases.
mysql> create database appm_regdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> create database appm_appdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> create database appm_esdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> create database appm_socialdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Step 1: Change datasources mentioned previously (other than the STATS_DB) as follows by pointing to above created MySQL databases. You need to replace the config with valid database username/password.
Note that <defaultAutoCommit>false</defaultAutoCommit> property is mandatory for "jdbc/WSO2AM_DB" datasource.
File location: {AppM_Home}/repository/conf/datasources/master-datasources.xml
<datasource>
<name>WSO2_CARBON_DB</name>
<description>The datasource used for registry and user manager</description>
<jndiConfig>
<name>jdbc/WSO2CarbonDB</name>
</jndiConfig>
<definition type="RDBMS">
<configuration>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/appm_regdb</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>root</password>
<driverClassName>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClassName>
<maxActive>50</maxActive>
<maxWait>60000</maxWait>
<testOnBorrow>true</testOnBorrow>
<validationQuery>SELECT 1</validationQuery>
<validationInterval>30000</validationInterval>
</configuration>
</definition>
</datasource>
<datasource>
<name>WSO2AM_DB</name>
<description>The datasource used for APP Manager database</description>
<jndiConfig>
<name>jdbc/WSO2AM_DB</name>
</jndiConfig>
<definition type="RDBMS">
<configuration>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/appm_appdb</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>root</password>
<driverClassName>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClassName>
<defaultAutoCommit>false</defaultAutoCommit>
<maxActive>50</maxActive>
<maxWait>60000</maxWait>
<testOnBorrow>true</testOnBorrow>
<validationQuery>SELECT 1</validationQuery>
<validationInterval>30000</validationInterval>
</configuration>
</definition>
</datasource>
<datasource>
<name>JAGH2</name>
<description>The datasource used for by the Jaggery Storage Manager</description>
<jndiConfig>
<name>jdbc/ES_Storage</name>
</jndiConfig>
<definition type="RDBMS">
<configuration>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/appm_esdb</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>root</password>
<driverClassName>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClassName>
<maxActive>50</maxActive>
<maxWait>60000</maxWait>
</configuration>
</definition>
</datasource>
<datasource>
<name>WSO2_SOCIAL_DB</name>
<description>The datasource used for social framework</description>
<jndiConfig>
<name>jdbc/WSO2SocialDB</name>
</jndiConfig>
<definition type="RDBMS">
<configuration>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/appm_socialdb</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>root</password>
<driverClassName>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClassName>
<maxActive>50</maxActive>
<maxWait>60000</maxWait>
<testOnBorrow>true</testOnBorrow>
<validationQuery>SELECT 1</validationQuery>
<validationInterval>30000</validationInterval>
</configuration>
</definition>
</datasource>
Step 2: Copy MySQL jdbc driver to {AppM_Home}/repository/components/lib directory
Step 3: Start the server with -Dsetup option. This will create the required tables in above four databases.
sh wso2server.sh -Dsetup
We have following five datasources defined in the {AppM_Home}/repository/conf/datasources/master-datasources.xml file.
[1] <name>jdbc/WSO2CarbonDB</name> - Use for registry data storage, user store, permission store
[2] <name>jdbc/WSO2AM_DB</name> - Use to store App details that created from App Manager
[3] <name>jdbc/WSO2AM_STATS_DB</name> - Stats storage. Needed only when Data Analytic Server is configured
[4] <name>jdbc/ES_Storage</name> - Use to store thumbnail/banner images of apps
[5] <name>jdbc/WSO2SocialDB</name> - Use to store comments and ratings added for apps by store users
This guide explains configuring App Manager standalone instance with MySQL DB. If it is a cluster deployment, there are some additional configurations required other than explains in this post.
Step 0: Login to the MySQL server and create 4 databases.
mysql> create database appm_regdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> create database appm_appdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> create database appm_esdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> create database appm_socialdb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Step 1: Change datasources mentioned previously (other than the STATS_DB) as follows by pointing to above created MySQL databases. You need to replace the config with valid database username/password.
Note that <defaultAutoCommit>false</defaultAutoCommit> property is mandatory for "jdbc/WSO2AM_DB" datasource.
File location: {AppM_Home}/repository/conf/datasources/master-datasources.xml
<datasource>
<name>WSO2_CARBON_DB</name>
<description>The datasource used for registry and user manager</description>
<jndiConfig>
<name>jdbc/WSO2CarbonDB</name>
</jndiConfig>
<definition type="RDBMS">
<configuration>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/appm_regdb</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>root</password>
<driverClassName>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClassName>
<maxActive>50</maxActive>
<maxWait>60000</maxWait>
<testOnBorrow>true</testOnBorrow>
<validationQuery>SELECT 1</validationQuery>
<validationInterval>30000</validationInterval>
</configuration>
</definition>
</datasource>
<datasource>
<name>WSO2AM_DB</name>
<description>The datasource used for APP Manager database</description>
<jndiConfig>
<name>jdbc/WSO2AM_DB</name>
</jndiConfig>
<definition type="RDBMS">
<configuration>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/appm_appdb</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>root</password>
<driverClassName>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClassName>
<defaultAutoCommit>false</defaultAutoCommit>
<maxActive>50</maxActive>
<maxWait>60000</maxWait>
<testOnBorrow>true</testOnBorrow>
<validationQuery>SELECT 1</validationQuery>
<validationInterval>30000</validationInterval>
</configuration>
</definition>
</datasource>
<datasource>
<name>JAGH2</name>
<description>The datasource used for by the Jaggery Storage Manager</description>
<jndiConfig>
<name>jdbc/ES_Storage</name>
</jndiConfig>
<definition type="RDBMS">
<configuration>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/appm_esdb</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>root</password>
<driverClassName>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClassName>
<maxActive>50</maxActive>
<maxWait>60000</maxWait>
</configuration>
</definition>
</datasource>
<datasource>
<name>WSO2_SOCIAL_DB</name>
<description>The datasource used for social framework</description>
<jndiConfig>
<name>jdbc/WSO2SocialDB</name>
</jndiConfig>
<definition type="RDBMS">
<configuration>
<url>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/appm_socialdb</url>
<username>root</username>
<password>root</password>
<driverClassName>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</driverClassName>
<maxActive>50</maxActive>
<maxWait>60000</maxWait>
<testOnBorrow>true</testOnBorrow>
<validationQuery>SELECT 1</validationQuery>
<validationInterval>30000</validationInterval>
</configuration>
</definition>
</datasource>
Step 2: Copy MySQL jdbc driver to {AppM_Home}/repository/components/lib directory
Step 3: Start the server with -Dsetup option. This will create the required tables in above four databases.
sh wso2server.sh -Dsetup
That's all.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)